Note
Click here to download the full example code
2.7.4.11. Gradient descent¶
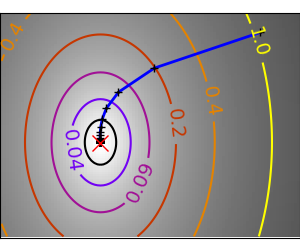
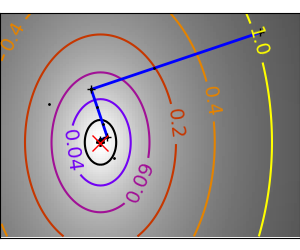
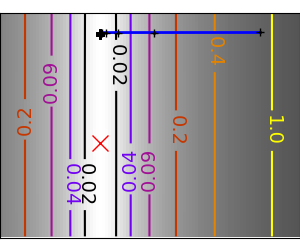
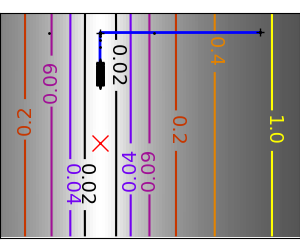
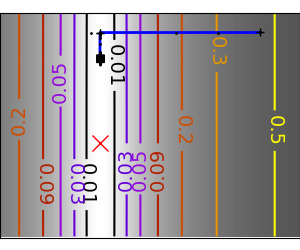
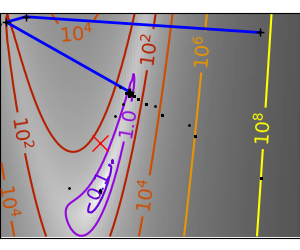
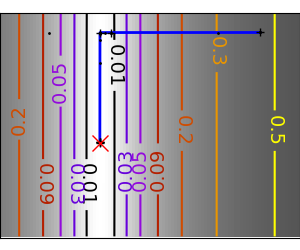
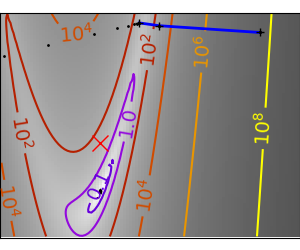
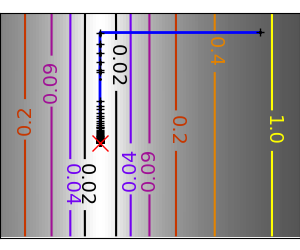
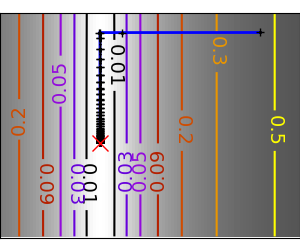
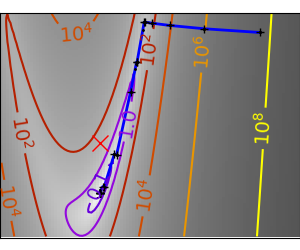
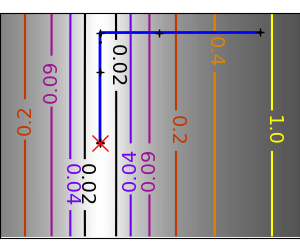
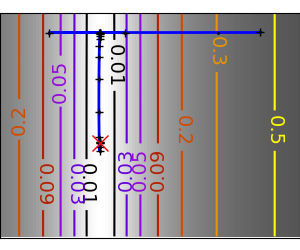
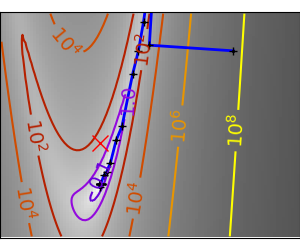
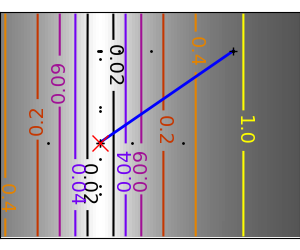
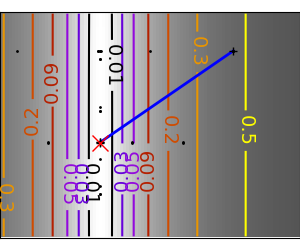
An example demoing gradient descent by creating figures that trace the evolution of the optimizer.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy import optimize
import sys, os
sys.path.append(os.path.abspath('helper'))
from cost_functions import mk_quad, mk_gauss, rosenbrock,\
rosenbrock_prime, rosenbrock_hessian, LoggingFunction,\
CountingFunction
x_min, x_max = -1, 2
y_min, y_max = 2.25/3*x_min - .2, 2.25/3*x_max - .2
A formatter to print values on contours
def super_fmt(value):
if value > 1:
if np.abs(int(value) - value) < .1:
out = '$10^{%.1i}$' % value
else:
out = '$10^{%.1f}$' % value
else:
value = np.exp(value - .01)
if value > .1:
out = '%1.1f' % value
elif value > .01:
out = '%.2f' % value
else:
out = '%.2e' % value
return out
A gradient descent algorithm do not use: its a toy, use scipy’s optimize.fmin_cg
def gradient_descent(x0, f, f_prime, hessian=None, adaptative=False):
x_i, y_i = x0
all_x_i = list()
all_y_i = list()
all_f_i = list()
for i in range(1, 100):
all_x_i.append(x_i)
all_y_i.append(y_i)
all_f_i.append(f([x_i, y_i]))
dx_i, dy_i = f_prime(np.asarray([x_i, y_i]))
if adaptative:
# Compute a step size using a line_search to satisfy the Wolf
# conditions
step = optimize.line_search(f, f_prime,
np.r_[x_i, y_i], -np.r_[dx_i, dy_i],
np.r_[dx_i, dy_i], c2=.05)
step = step[0]
if step is None:
step = 0
else:
step = 1
x_i += - step*dx_i
y_i += - step*dy_i
if np.abs(all_f_i[-1]) < 1e-16:
break
return all_x_i, all_y_i, all_f_i
def gradient_descent_adaptative(x0, f, f_prime, hessian=None):
return gradient_descent(x0, f, f_prime, adaptative=True)
def conjugate_gradient(x0, f, f_prime, hessian=None):
all_x_i = [x0[0]]
all_y_i = [x0[1]]
all_f_i = [f(x0)]
def store(X):
x, y = X
all_x_i.append(x)
all_y_i.append(y)
all_f_i.append(f(X))
optimize.minimize(f, x0, jac=f_prime, method="CG", callback=store, options={"gtol": 1e-12})
return all_x_i, all_y_i, all_f_i
def newton_cg(x0, f, f_prime, hessian):
all_x_i = [x0[0]]
all_y_i = [x0[1]]
all_f_i = [f(x0)]
def store(X):
x, y = X
all_x_i.append(x)
all_y_i.append(y)
all_f_i.append(f(X))
optimize.minimize(f, x0, method="Newton-CG", jac=f_prime, hess=hessian, callback=store, options={"xtol": 1e-12})
return all_x_i, all_y_i, all_f_i
def bfgs(x0, f, f_prime, hessian=None):
all_x_i = [x0[0]]
all_y_i = [x0[1]]
all_f_i = [f(x0)]
def store(X):
x, y = X
all_x_i.append(x)
all_y_i.append(y)
all_f_i.append(f(X))
optimize.minimize(f, x0, method="BFGS", jac=f_prime, callback=store, options={"gtol": 1e-12})
return all_x_i, all_y_i, all_f_i
def powell(x0, f, f_prime, hessian=None):
all_x_i = [x0[0]]
all_y_i = [x0[1]]
all_f_i = [f(x0)]
def store(X):
x, y = X
all_x_i.append(x)
all_y_i.append(y)
all_f_i.append(f(X))
optimize.minimize(f, x0, method="Powell", callback=store, options={"ftol": 1e-12})
return all_x_i, all_y_i, all_f_i
def nelder_mead(x0, f, f_prime, hessian=None):
all_x_i = [x0[0]]
all_y_i = [x0[1]]
all_f_i = [f(x0)]
def store(X):
x, y = X
all_x_i.append(x)
all_y_i.append(y)
all_f_i.append(f(X))
optimize.minimize(f, x0, method="Nelder-Mead", callback=store, options={"ftol": 1e-12})
return all_x_i, all_y_i, all_f_i
Run different optimizers on these problems
levels = dict()
for index, ((f, f_prime, hessian), optimizer) in enumerate((
(mk_quad(.7), gradient_descent),
(mk_quad(.7), gradient_descent_adaptative),
(mk_quad(.02), gradient_descent),
(mk_quad(.02), gradient_descent_adaptative),
(mk_gauss(.02), gradient_descent_adaptative),
((rosenbrock, rosenbrock_prime, rosenbrock_hessian),
gradient_descent_adaptative),
(mk_gauss(.02), conjugate_gradient),
((rosenbrock, rosenbrock_prime, rosenbrock_hessian),
conjugate_gradient),
(mk_quad(.02), newton_cg),
(mk_gauss(.02), newton_cg),
((rosenbrock, rosenbrock_prime, rosenbrock_hessian),
newton_cg),
(mk_quad(.02), bfgs),
(mk_gauss(.02), bfgs),
((rosenbrock, rosenbrock_prime, rosenbrock_hessian),
bfgs),
(mk_quad(.02), powell),
(mk_gauss(.02), powell),
((rosenbrock, rosenbrock_prime, rosenbrock_hessian),
powell),
(mk_gauss(.02), nelder_mead),
((rosenbrock, rosenbrock_prime, rosenbrock_hessian),
nelder_mead),
)):
# Compute a gradient-descent
x_i, y_i = 1.6, 1.1
counting_f_prime = CountingFunction(f_prime)
counting_hessian = CountingFunction(hessian)
logging_f = LoggingFunction(f, counter=counting_f_prime.counter)
all_x_i, all_y_i, all_f_i = optimizer(np.array([x_i, y_i]),
logging_f, counting_f_prime,
hessian=counting_hessian)
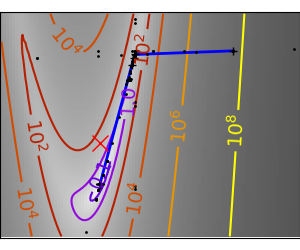
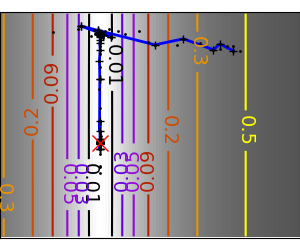
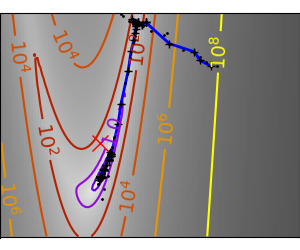
# Plot the contour plot
if not max(all_y_i) < y_max:
x_min *= 1.2
x_max *= 1.2
y_min *= 1.2
y_max *= 1.2
x, y = np.mgrid[x_min:x_max:100j, y_min:y_max:100j]
x = x.T
y = y.T
plt.figure(index, figsize=(3, 2.5))
plt.clf()
plt.axes([0, 0, 1, 1])
X = np.concatenate((x[np.newaxis, ...], y[np.newaxis, ...]), axis=0)
z = np.apply_along_axis(f, 0, X)
log_z = np.log(z + .01)
plt.imshow(log_z,
extent=[x_min, x_max, y_min, y_max],
cmap=plt.cm.gray_r, origin='lower',
vmax=log_z.min() + 1.5*log_z.ptp())
contours = plt.contour(log_z,
levels=levels.get(f, None),
extent=[x_min, x_max, y_min, y_max],
cmap=plt.cm.gnuplot, origin='lower')
levels[f] = contours.levels
plt.clabel(contours, inline=1,
fmt=super_fmt, fontsize=14)
plt.plot(all_x_i, all_y_i, 'b-', linewidth=2)
plt.plot(all_x_i, all_y_i, 'k+')
plt.plot(logging_f.all_x_i, logging_f.all_y_i, 'k.', markersize=2)
plt.plot([0], [0], 'rx', markersize=12)
plt.xticks(())
plt.yticks(())
plt.xlim(x_min, x_max)
plt.ylim(y_min, y_max)
plt.draw()
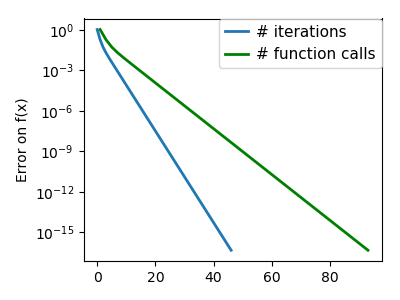
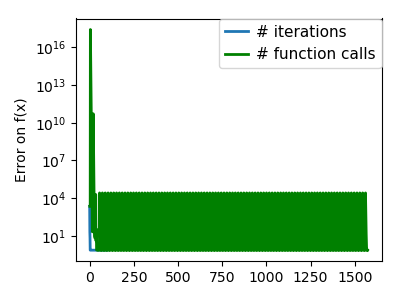
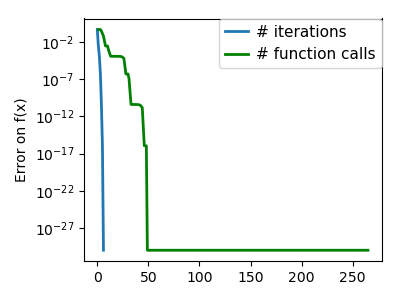
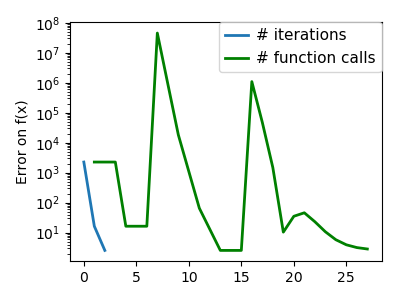
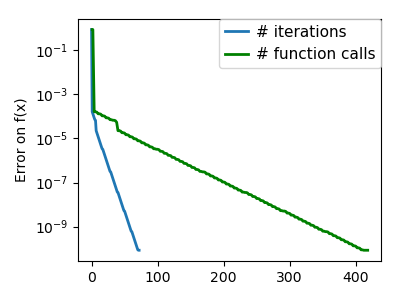
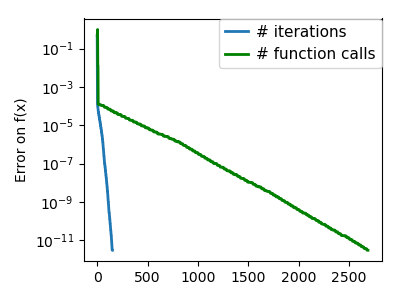
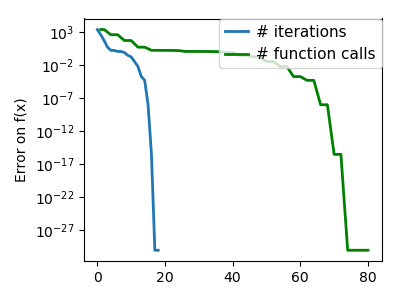
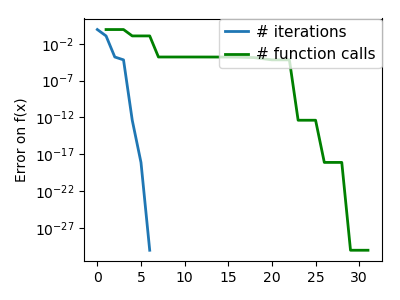
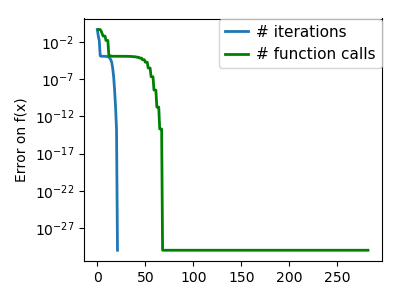
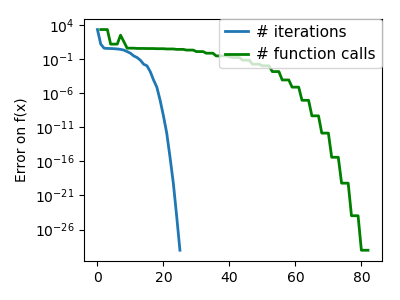
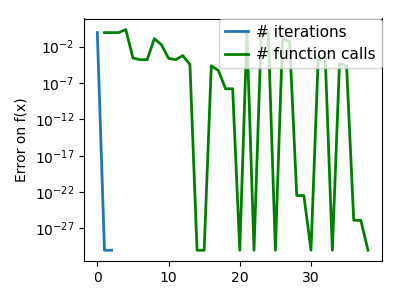
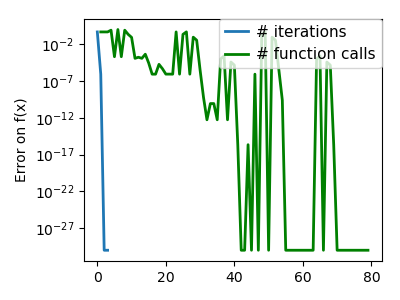
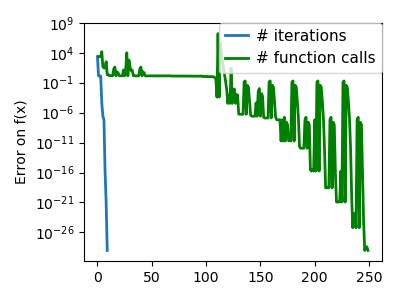
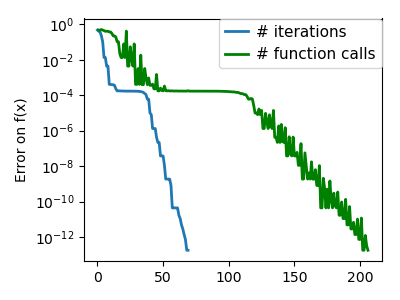
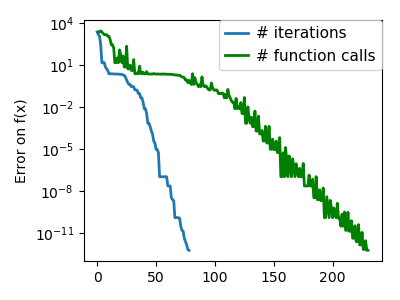
plt.figure(index + 100, figsize=(4, 3))
plt.clf()
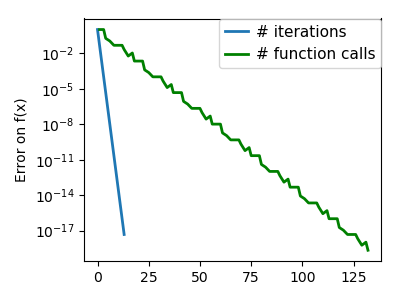
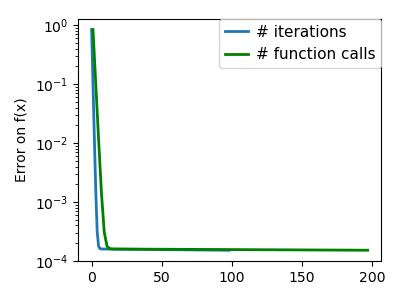
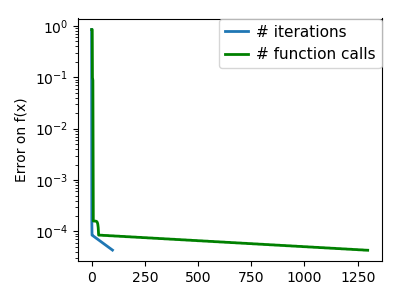
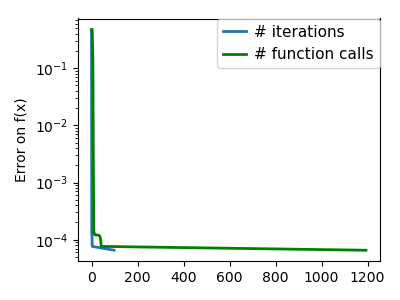
plt.semilogy(np.maximum(np.abs(all_f_i), 1e-30), linewidth=2,
label='# iterations')
plt.ylabel('Error on f(x)')
plt.semilogy(logging_f.counts,
np.maximum(np.abs(logging_f.all_f_i), 1e-30),
linewidth=2, color='g', label='# function calls')
plt.legend(loc='upper right', frameon=True, prop=dict(size=11),
borderaxespad=0, handlelength=1.5, handletextpad=.5)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.draw()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 10.373 seconds)